Semantic search blindspots
Judgment, detection & correction
Imagine a shopper searching for a "birthday gift" in your online commerce store, expecting to find various thoughtful options. Instead, they’re greeted with a random assortment of unrelated products like kitchen appliances, gardening tools, and office supplies. Frustrated, they leave your site and take their business elsewhere. This common scenario highlights the critical importance of effective semantic search in online commerce.
Semantic search is impressive; it’s revolutionized how shoppers find products in commerce search by understanding the intent behind their searches. It moves beyond simple keyword matching and looks at the context, shopper behavior, and even the nuances of language to deliver more accurate results. However, despite its advanced capabilities, semantic search is not perfect and can sometimes miss the mark. Due to various limitations and complexities inherent in understanding human language and intent, these misses are what we call semantic search blindspots.
Semantic search blindspots are gaps or errors in the search results where the system fails to accurately interpret or match the shopper's intent with the relevant products. These blindspots can occur for several reasons:
- Ambiguity in language: Shoppers often use ambiguous terms or phrases that can have multiple meanings. For example, a search for "apple" could refer to the fruit or the tech company.
- Context misinterpretation: The search engine might misunderstand the context in which a query is made. For instance, searching for "jaguar" could refer to the animal, the car brand, or even a sports team, depending on the context.
- Synonym overlook: Shoppers may use different terms to refer to the same product. If the search engine doesn’t recognize synonyms effectively, it might miss relevant items, such as "sneakers" vs. "trainers."
- Evolving language and trends: Language and shopping preferences evolve over time. New terms, slang, or trending products can create blindspots if the search algorithm isn't regularly updated.
- Complex queries: Multi-faceted queries that combine different product attributes or preferences can be challenging. For example, "affordable eco-friendly running shoes" requires the search engine to understand and prioritize multiple criteria.
As a merchant, you must identify and address these blindspots to enhance your shoppers’ search experience. Ignoring them can lead to user frustration, higher bounce rates, and lost sales opportunities. By understanding the nature of these blindspots, you can better prepare your search system to handle the complexity of human language and intent. In this blog post, we want to guide you through some great tips on detecting and correcting these blindspots so you can take your commerce search experience to the next level.
Judge semantic search effectiveness
Based on what’s popularly said, “If you cannot measure it, you cannot improve it,” you must first measure your search performance to evaluate and judge its effectiveness. But you need to measure the right things and measure them right so you’ll have a clear set of metrics to assess how well your search is doing. Here are some steps to get you started:
- Understand your shoppers' intent: Use natural language processing (NLP) to understand better what shoppers are actually looking for.
- Evaluate the relevance of results: Determine if the results returned by the semantic search engine are what the shopper had in mind. This requires a combination of implicit and explicit feedback.
Detect and fix blindspots with feedback and evaluations
Detecting blindspots in semantic search requires a methodical approach to understanding where and why the search engine fails to meet shoppers’ expectations. By leveraging user feedback and offline evaluation capabilities, you can identify and revise the weak points in your search system.
Implicit and explicit feedback
There are two primary types of feedback to consider: implicit and explicit.
Implicit feedback is gathered from shopper interactions such as clicks, purchases, and other engagement metrics. It's valuable because it shows actual shopper behavior. However, it can be influenced by several factors, like position bias (where items at the top of the list get more clicks) and the newness of products (new items haven't had time to gather clicks).
For example, if shoppers frequently click on a product that appears fifth in the search results, it might indicate that the product is highly relevant but positioned too low in the results.
On the other hand, explicit feedback involves asking merchants, retailers, or other stakeholders to manually label the relevance of search results. This is more accurate but can be tedious and labor-intensive. However, explicit feedback can also involve synthetic labeling from AI, which can automate and streamline the process. It also depends on having full context and understanding of the queries. For example, you review search results for the “running shoes” query and manually mark which results are relevant and which are not. This manually labeled dataset can be used to:
- Establish a ground truth to evaluate the relevance of results and understand your shoppers' intent.
- Feedback the algorithm to adjust the semantic search solution.
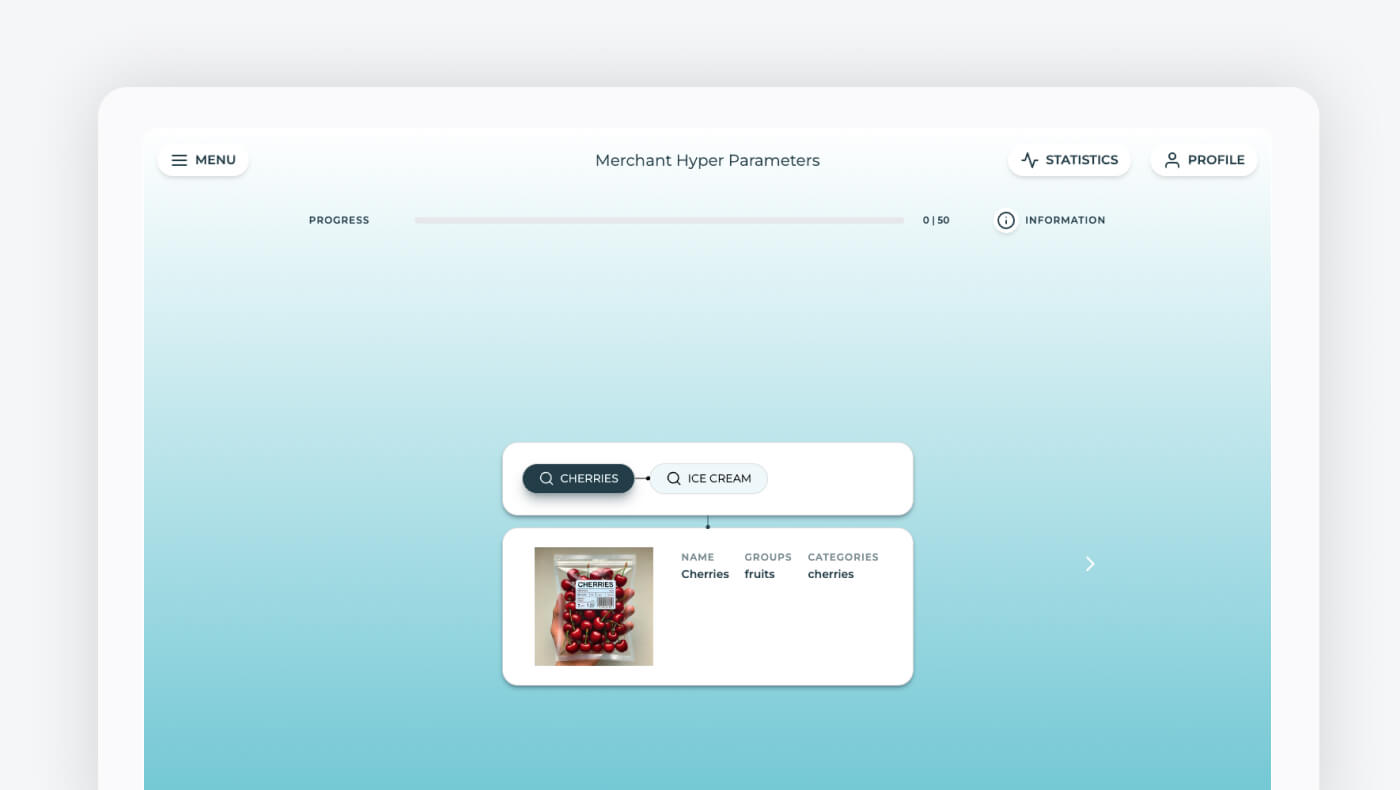
Fig. Empathy Platform's Judge the Judgements POC
Even though this method turns out to be a very trustworthy source for detecting (and even correcting) blindspots, traditionally explicit feedback was a tedious, repetitive, and challenging process based on evaluating numerous queries from heavy spreadsheets. That’s why we have developed the Judge the Judgment new tool to help data scientists, merchants, and retailers manually evaluate the relevance of search results in a very easy and user-friendly way. This new tool helps categorize results as highly relevant, partially relevant, or irrelevant, fine-tuning the semantic search effectiveness to better meet shoppers’ expectations.
Offline evaluations
You can use feedback not only for training, refining, and improving your semantic search models but also for creating evaluation datasets to figure out how your search will perform in a continuous improvement ranking strategy. You can then use these evaluation datasets to perform offline evaluations.
Offline evaluations are an effective method for correcting blindspots in a non-productized environment. This method uses evaluation datasets to test and refine your search, predict how semantics will perform, and detect failure patterns within your datasets. For example, through an offline evaluation process, you can discover that search results for "summer dresses" often miss products in the new arrivals category. This insight leads to adjusting the algorithm to prioritize newer products.
Leveraging technology and continuous improvement
Using tools based on judgments and offline evaluations, you can streamline the process of detecting and fixing blindspots in your semantic search engine. By integrating these tools, you can automate parts of the feedback collection, making it less tedious and more scalable. You can measure, compare, and adjust search results effectively, ensuring your search engine is continuously learning and improving.
For example, Empathy Platform hybrid search system might automatically flag and correct a blindspot in which searches for “smartphone accessories” are dominated by phone cases, neglecting other relevant items like chargers and headphones.
Remember, the goal is to refine your search capabilities continuously. Regularly updating your dataset and using implicit and explicit feedback can improve the accuracy and relevance of your search results. This will help you stay ahead of trends and ensure your shoppers always find what they want.
For example, if regular updates to the dataset and feedback mechanisms reveal an emerging trend when shoppers search for eco-friendly products, the search algorithm can then be adjusted to better capture and prioritize these items.
In conclusion, detecting and correcting semantic search blindspots is an ongoing process. You can significantly enhance your commerce store search capabilities by measuring performance, gathering implicit and explicit feedback, and leveraging advanced tools for offline evaluation. This not only improves your shoppers’ experience, but also drives better business outcomes. Keep measuring, keep improving, and watch your search performance soar!
Embrace an hybrid-search free of flaws
Embrace the power of a hybrid search strategy, combining keyword and semantic search —free of flaws with feedback and offline evaluation strategies— and transform the way shoppers find what they need in your store. This approach ensures a well-rounded set of results, minimizing blindspots and maximizing relevance. Want to know more about how Empathy Platform approaches hybrid search? Don’t miss Understand semantics and vectors.
Open Innovation innitiatives
Empathy is constantly innovating and ideating through Open Innovation initiatives that foster the development of AI-based, cutting-edge, built-in-public technologies that are driven by market evolution needs. Today's story is part of this Open Innovation. Like many of the features, tools, and functionalities finally implemented within Empathy Platform, their foundations lie in Open Innovation projects. Keep an eye on Open Innovations webpage (opens new window) and Empathy Holdings' roadmap (opens new window) to not miss anything!